| 123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899100101102103104105106107108109110111112113114115116117118119120 |
- <!--
- title: "Monitor Pi-hole (and a Raspberry Pi) with Netdata"
- sidebar_label: "Monitor Pi-hole (and a Raspberry Pi) with Netdata"
- description: "Monitor Pi-hole metrics, plus Raspberry Pi system metrics, in minutes and completely for free with Netdata's open-source monitoring agent."
- image: /img/seo/guides/monitor/netdata-pi-hole-raspberry-pi.png
- custom_edit_url: https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/guides/monitor/pi-hole-raspberry-pi.md
- learn_status: "Published"
- learn_rel_path: "Miscellaneous"
- -->
- # Monitor Pi-hole (and a Raspberry Pi) with Netdata
- import { OneLineInstallWget } from '@site/src/components/OneLineInstall/'
- Between intrusive ads, invasive trackers, and vicious malware, many techies and homelab enthusiasts are advancing their
- networks' security and speed with a tiny computer and a powerful piece of software: [Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/).
- Pi-hole is a DNS sinkhole that prevents unwanted content from even reaching devices on your home network. It blocks ads
- and malware at the network, instead of using extensions/add-ons for individual browsers, so you'll stop seeing ads in
- some of the most intrusive places, like your smart TV. Pi-hole can even [improve your network's speed and reduce
- bandwidth](https://discourse.pi-hole.net/t/will-pi-hole-slow-down-my-network/2048).
- Most Pi-hole users run it on a [Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-4-model-b/) (hence the
- name), a credit card-sized, super-capable computer that costs about $35.
- And to keep tabs on how both Pi-hole and the Raspberry Pi are working to protect your network, you can use the
- open-source [Netdata monitoring agent](https://github.com/netdata/netdata).
- To get started, all you need is a [Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-4-model-b/) with
- Raspbian installed. This guide uses a Raspberry Pi 4 Model B and Raspbian GNU/Linux 10 (buster). This guide assumes
- you're connecting to a Raspberry Pi remotely over SSH, but you could also complete all these steps on the system
- directly using a keyboard, mouse, and monitor.
- ## Why monitor Pi-hole and a Raspberry Pi with Netdata?
- Netdata helps you monitor and troubleshoot all kinds of devices and the applications they run, including IoT devices
- like the Raspberry Pi and applications like Pi-hole.
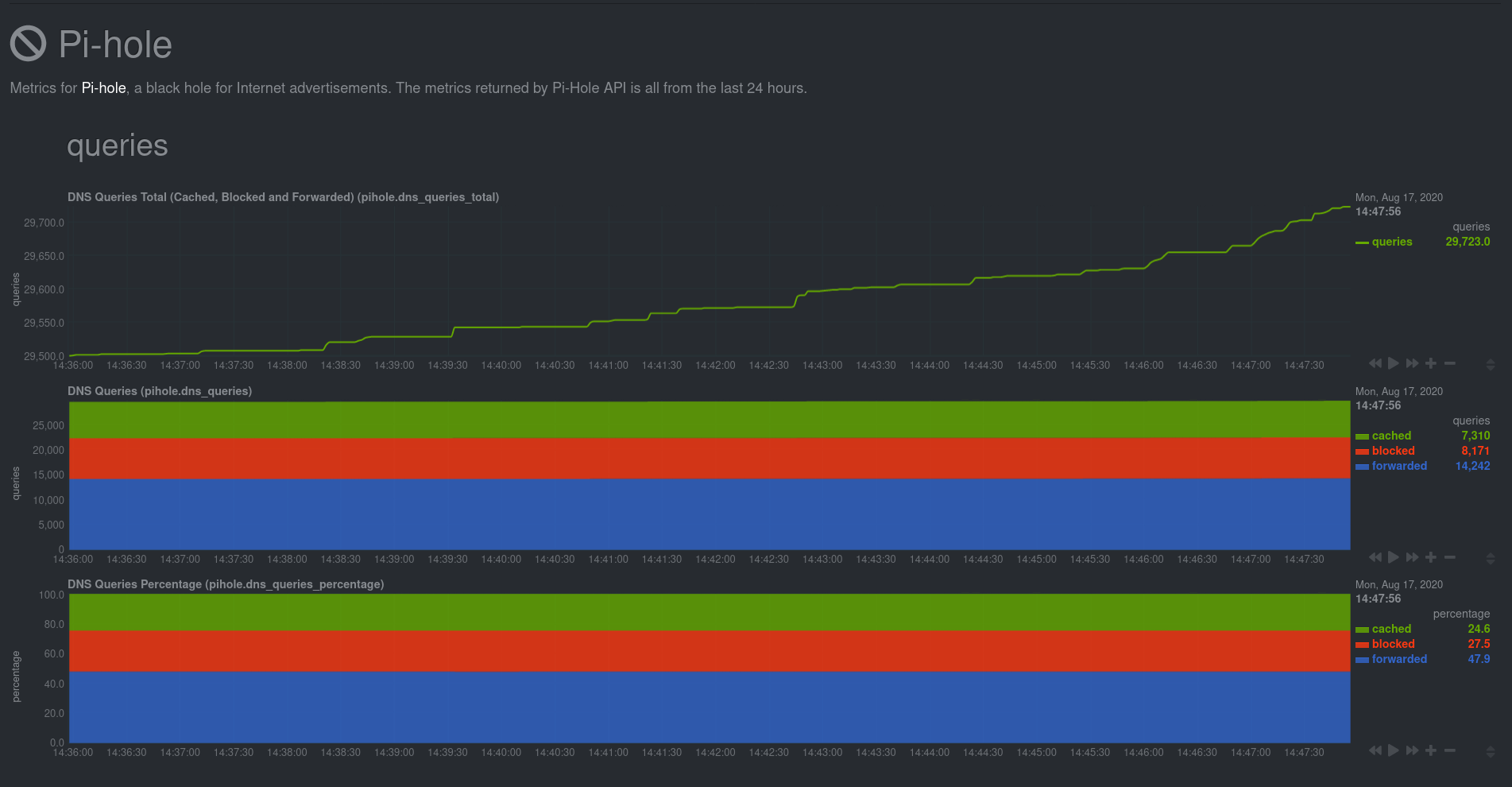
- After a two-minute installation and with zero configuration, you'll be able to see all of Pi-hole's metrics, including
- the volume of queries, connected clients, DNS queries per type, top clients, top blocked domains, and more.
- With Netdata installed, you can also monitor system metrics and any other applications you might be running. By default,
- Netdata collects metrics on CPU usage, disk IO, bandwidth, per-application resource usage, and a ton more. With the
- Raspberry Pi used for this guide, Netdata automatically collects about 1,500 metrics every second!
- 
- ## Install Netdata
- Let's start by installing Netdata first so that it can start collecting system metrics as soon as possible for the most
- possible historic data.
- > ⚠️ Don't install Netdata using `apt` and the default package available in Raspbian. The Netdata team does not maintain
- > this package, and can't guarantee it works properly.
- On Raspberry Pis running Raspbian, the best way to install Netdata is our one-line kickstart script. This script asks
- you to install dependencies, then compiles Netdata from source via [GitHub](https://github.com/netdata/netdata).
- <OneLineInstallWget/>
- Once installed on a Raspberry Pi 4 with no accessories, Netdata starts collecting roughly 1,500 metrics every second and
- populates its dashboard with more than 250 charts.
- Open your browser of choice and navigate to `http://NODE:19999/`, replacing `NODE` with the IP address of your Raspberry
- Pi. Not sure what that IP is? Try running `hostname -I | awk '{print $1}'` from the Pi itself.
- You'll see Netdata's dashboard and a few hundred real-time, interactive charts. Feel free to explore, but let's turn our attention to installing Pi-hole.
- ## Install Pi-Hole
- Like Netdata, Pi-hole has a one-line script for simple installation. From your Raspberry Pi, run the following:
- ```bash
- curl -sSL https://install.pi-hole.net | bash
- ```
- The installer will help you set up Pi-hole based on the topology of your network. Once finished, you should set up your
- devices—or your router for system-wide sinkhole protection—to [use Pi-hole as their DNS
- service](https://discourse.pi-hole.net/t/how-do-i-configure-my-devices-to-use-pi-hole-as-their-dns-server/245). You've
- finished setting up Pi-hole at this point.
- As far as configuring Netdata to monitor Pi-hole metrics, there's nothing you actually need to do. Netdata's [Pi-hole
- collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/collector/pihole/README.md) will autodetect the new service
- running on your Raspberry Pi and immediately start collecting metrics every second.
- Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, which will then recognize that Pi-hole is running and start a
- per-second collection job. When you refresh your Netdata dashboard or load it up again in a new tab, you'll see a new
- entry in the menu for **Pi-hole** metrics.
- ## Use Netdata to explore and monitor your Raspberry Pi and Pi-hole
- By the time you've reached this point in the guide, Netdata has already collected a ton of valuable data about your
- Raspberry Pi, Pi-hole, and any other apps/services you might be running. Even a few minutes of collecting 1,500 metrics
- per second adds up quickly.
- You can now use Netdata's synchronized charts to zoom, highlight, scrub through time, and discern how an anomaly in one
- part of your system might affect another.
- 
- ### Storing historical metrics on your Raspberry Pi
- By default, Netdata allocates 256 MiB in disk space to store historical metrics inside the [database
- engine](/src/database/engine/README.md). On the Raspberry Pi used for this guide, Netdata collects 1,500 metrics every
- second, which equates to storing 3.5 days worth of historical metrics.
- You can increase this allocation by editing `netdata.conf` and increasing the `dbengine multihost disk space` setting to
- more than 256.
- ```yaml
- [global]
- dbengine multihost disk space = 512
- ```
- Use our [database sizing
- calculator](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md#calculate-the-system-resources-ram-disk-space-needed-to-store-metrics)
- and the [Database configuration documentation](/src/database/README.md) to help you determine the right
- setting for your Raspberry Pi.
|